
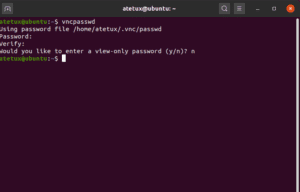
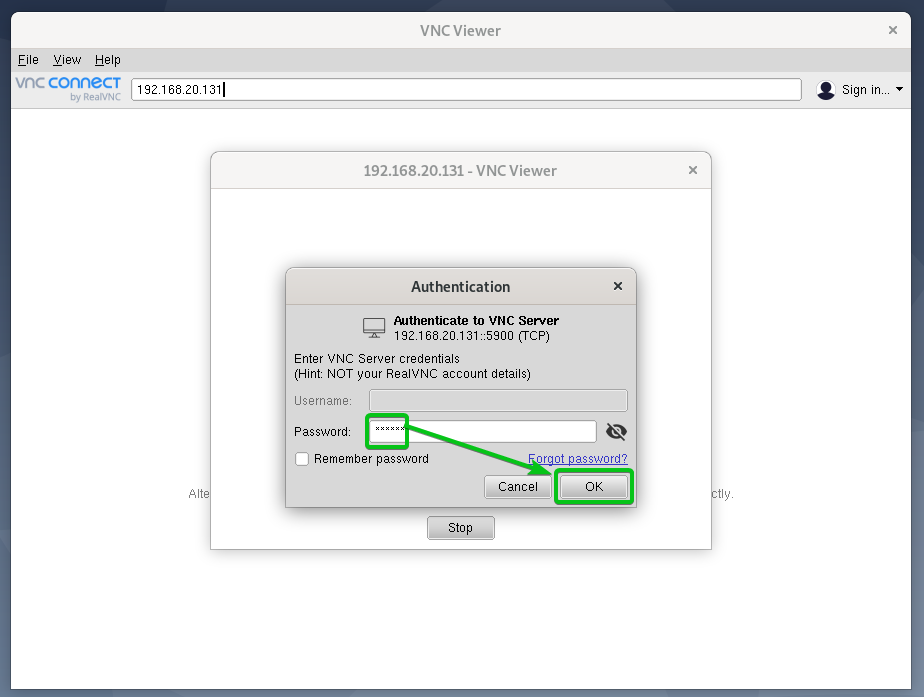
ssh -L 59000:localhost: 5901 -C -N -l sammy your_server_ip.You can do this via the terminal on Linux or macOS with the following ssh command: To securely connect to your server, you’ll establish an SSH tunnel and then tell your VNC client to connect using that tunnel rather than making a direct connection.Ĭreate an SSH connection on your local computer that securely forwards to the localhost connection for VNC. This port is called a display port, and is referred to by VNC as :1: Step 3 - Connecting to the VNC Desktop Securely Here, you can see that the command launches a default server instance on port 5901. Log file is /home/ sammy/.vnc/ your_hostname:1.log Starting applications specified in /home/ sammy/.vnc/xstartup You’ll be prompted to enter and verify a password to access your machine remotely: Next, run the vncpasswd command to set a VNC access password and create the initial configuration files: Once that installation completes, install the TightVNC server: Then install Xfce along with the xfce4-goodies package, which contains a few enhancements for the desktop environment: Step 1 - Installing the Desktop Environment and VNC ServerĪfter connecting to your server with SSH, update your list of packages: On Linux, you can choose from many options, including vinagre, krdc, RealVNC, or TightVNC.On macOS, you can use the built-in Screen Sharing program, or can use a cross-platform app like RealVNC.On Windows, you can use TightVNC, RealVNC, or UltraVNC.The VNC client you use must support connections over SSH tunnels:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
